Svalbard Wastewater Case Study
Case Study Components
Introduction to the Site
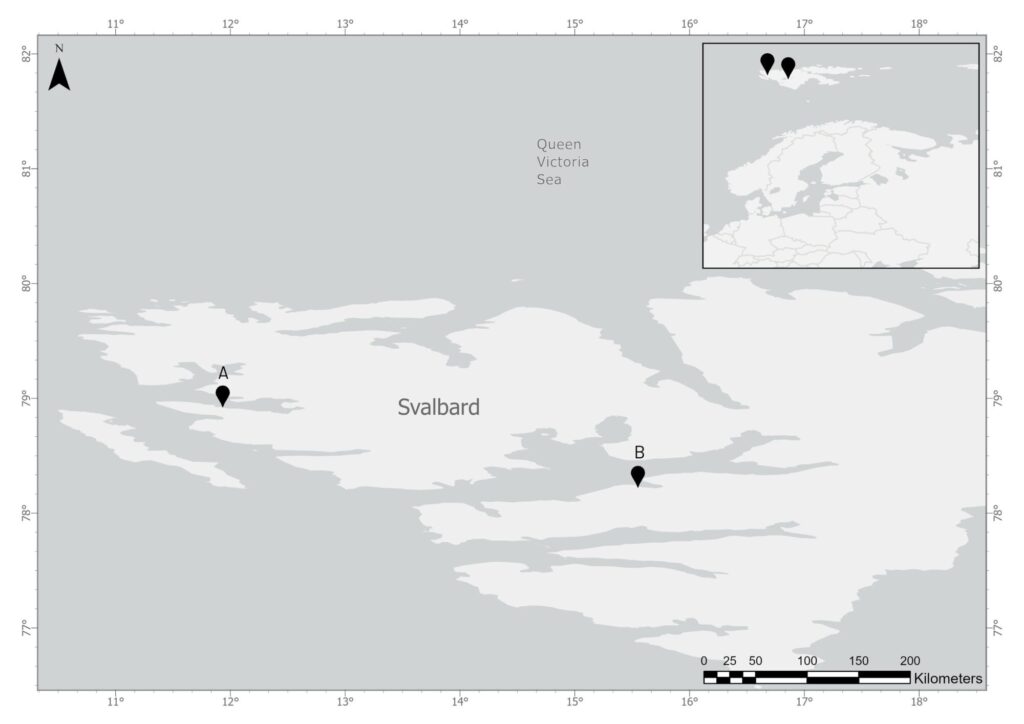
Location: 78.2403 N, 15.5956 W
Observed ecosystem changes
Poor benthic ecosystem integrity due to discharge of untreated wastewater
CLIMAREST Objectives
Find solutions to support the recovery of benthic ecosystems in Arctic fjords affected by untreated or minimally treated wastewater.
Features of Svalbard
Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean
Hosts several permanent settlements and research stations
Seeing increasing environmental pressures due to increased tourism, climate change, and lack of adequate sanitation facilities
Map indicating the location of Adventfjorden, located outside of Longyearbyen, the most populous settlement on Svalbard.
Driving Factors and Motivations
Benthic communities are essential components of marine ecosystems. Due to a lack of access to proper treatment facilities, over 300,000m3 of untreated wastewater are being discharged into Adventfjorden per year, negatively affecting these critical habitats.
Aims of restoration efforts
- Developing, testing, and demonstrating solutions to support the recovery of benthic ecosystems

Assessment Phase
Key features of wastewater treatment near Adventfjorden
December 2022: Wastewater treatment begins for the first time
Screen installed to remove macrowaste (>6mm in diameter)
- Dissolved or fine particular pollutants still pass into the fjord (chemicals, pharmaceuticals, microplastics, etc.)
Wastewater and pollutant load highly variable and seasonal due to tourism
- Highest visitor numbers reported February-August
- Local population numbers around 2000, but Longyearbyen alone receives up to 150 000 tourists per year

Planning and Design Phase
Primary Objective: Reduce pressure on coastal marine ecosystems due to wastewater discharge by raising awareness among the local population and visitors that everything flushed down the toilet ends up in the fjord
Legal Contracting/Permits
Longyearbyen Community Council
- Assisted in defining the format and content of the social awareness campaign
- Contracted SINTEF to conduct periodic assessments of water and sediment quality in areas affected by wastewater discharge
Relevant EU Regulations
EU Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive
Local Collaborations
Visit Svalbard and hotels
- Assisted in defining/co-creating the content of the social awareness campaign
Hotels, bars, restaurants, and tourist centres
- Involved in the social awareness campaign:
- Placed "Protect Our Waters" stickers into toilet areas
- Showed short informational videos when possible
- Displayed and promoted QR codes linked to a social awareness campaign survey
Developing Project Protocols
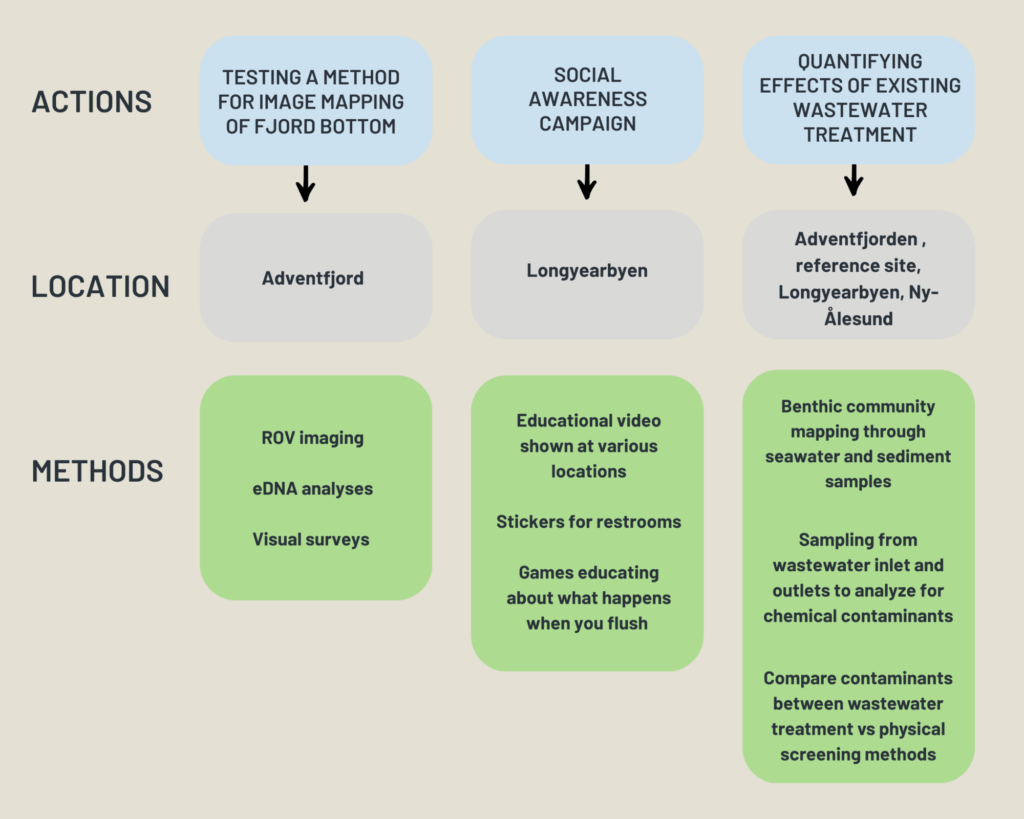

Implementation Phase
Implementation Process
Raise awareness and get public support for advanced wastewater treatment
- Provide information to community members and decision-makers about
- Available treatment technologies
- Efficacy and appropriateness for application in the local context
Establish several water sampling sites
- Sample along a longitudinal transect from the point of wastewater discharge
- Control site (Ny-Ålesund with appropriate wastewater treatment)
- Reference site in an analogous fjord receiving no wastewater discharge
Complete benthic community status mapping at the test site and reference site
- Analyze seawater and sediment samples along same transect lines as other sampling
Collect water samples from test and control site for analysis of chemical contaminants
- Evaluate the efficacy of contaminant removal during wastewater treatment
- Examples of measurements: Nutrients, inorganic compounds, organic compounds
Conduct benthic faunal analysis on sediment samples
- Assessed contaminants
- Macrowaste (sanitary napkins, cotton buds, etc.)
- Microplastics
- Pharmaceuticals
- Other organic compounds of concern
Assess benthic biodiversity
- Visual surveys
- eDNA analysis
- ROV imaging
Monitoring and Data Collection Process
Monitoring: Social awareness campaign
Survey results assessing reach of the social awareness campaign
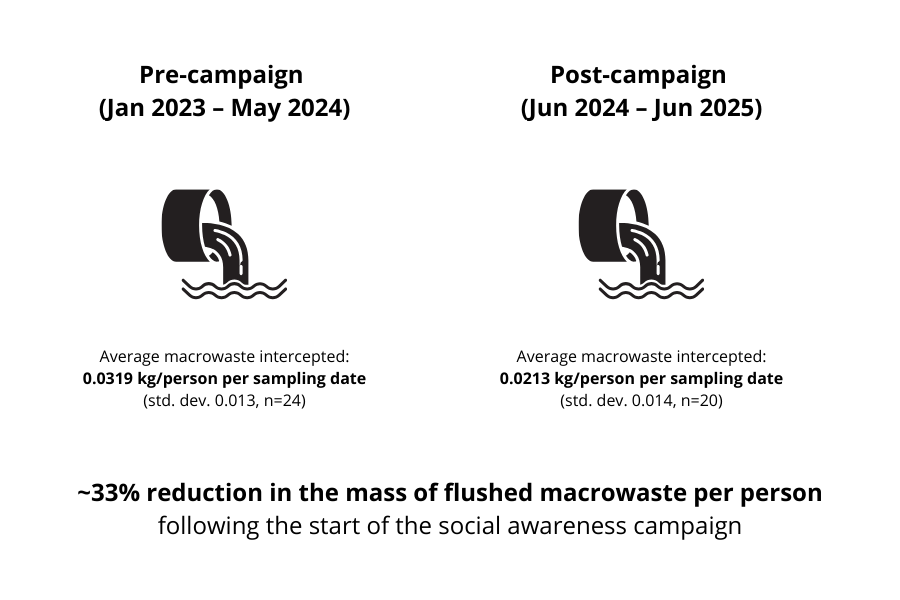
Weighing mass of macrowaste captured by the 6 mm screen at the Longyearbyen wastewater facility

Monitoring: Benthic community and biodiversity
Seawater, sediment, and sewage samples and biodiversity data compared with baseline data and information from previous studies

Restoration indicators measured
Macrowaste per square metre fjord sediment
Biodiversity as measured by eDNA of sediments
Biodiversity per taxonomic analysis
Foraminifera abundance & diversity (exp(H’)bc)
Ecological Quality Ratio in comparison with reference site
Mass of macrowaste (>6 mm) captured by screen at Longyearbyen wastewater collection facility (kg/week)
Proportion of survey respondents aware of the “Protect Our Waters” campaign (%)
Proportion of survey respondents aware that wastewater is discharged directly to the fjord (%)
Willingness to pay for wastewater treatment (NOK)

Ongoing Management, Monitoring, and Evaluation Phase
Initial results from the demonstration site